The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existHave students create a diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect using paper, markers, etc Tell them that they will be asked to go home and explain the Greenhouse Effect and global warming to a family member using their diagram as part of a homework assignment Have them practice presenting global warming using their diagrams with peer partnersT he greenhouse effect is the name applied to the process which causes the surface of the Earth to be warmer than it would have been in the absence of an atmosphere (Unfortunately, the name, greenhouse effect is a misnomer more on that later) Global warming is the name given to an expected increase in the magnitude of the greenhouse
What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub
Greenhouse effect diagram house
Greenhouse effect diagram house-A greenhouse is for growing plants It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight But why not just put the plants outside?Browse 234,977 greenhouse effect stock photos and images available or search for greenhouse effect diagram or greenhouse effect illustration to find more great stock photos and pictures Man on a rooftop looks at approaching flames as the Springs fire continues to grow on near Camarillo, California



The Greenhouse Effect And Earth S Energy Budget Energy Education
A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm Greenhouse Atmosphere Let's Heat Things Up!The diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surface Some heat escapes into space
Greenhouse Effect Diagram Worksheet Educationcom Global warming is a serious issue in our world today Help your child understand how it works with this greenhouse effect coloring worksheet Saved by Educationcom 3The greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent itAnd other greenhouse gases are building up in the atmosphere, essentially creating a "blanket" trapping excess heat near the Earth's surface (an effect known as global warming)3 The Earth's surface temperature warmed more during the last century than any other century during the last thousand T HE PROBLEM OF GLOBAL WARMING
The "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect worksAnother version of a greenhouse is what happens inside an automobile parked in the sun The sun's light and heat gets into the vehicle and is trapped inside, like the plastic bag around the jar The temperature inside a car can get over 1 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees If the greenhouse effect didn't exist, the average temperature of the earth would decrease from 14C (57F) to the lowest being 18C (04F) There are layers of greenhouse gases Some are carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrous oxide These act like a thermal blanket for the Earth They absorb heat and warm the surface for an average of 59




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Worksheet
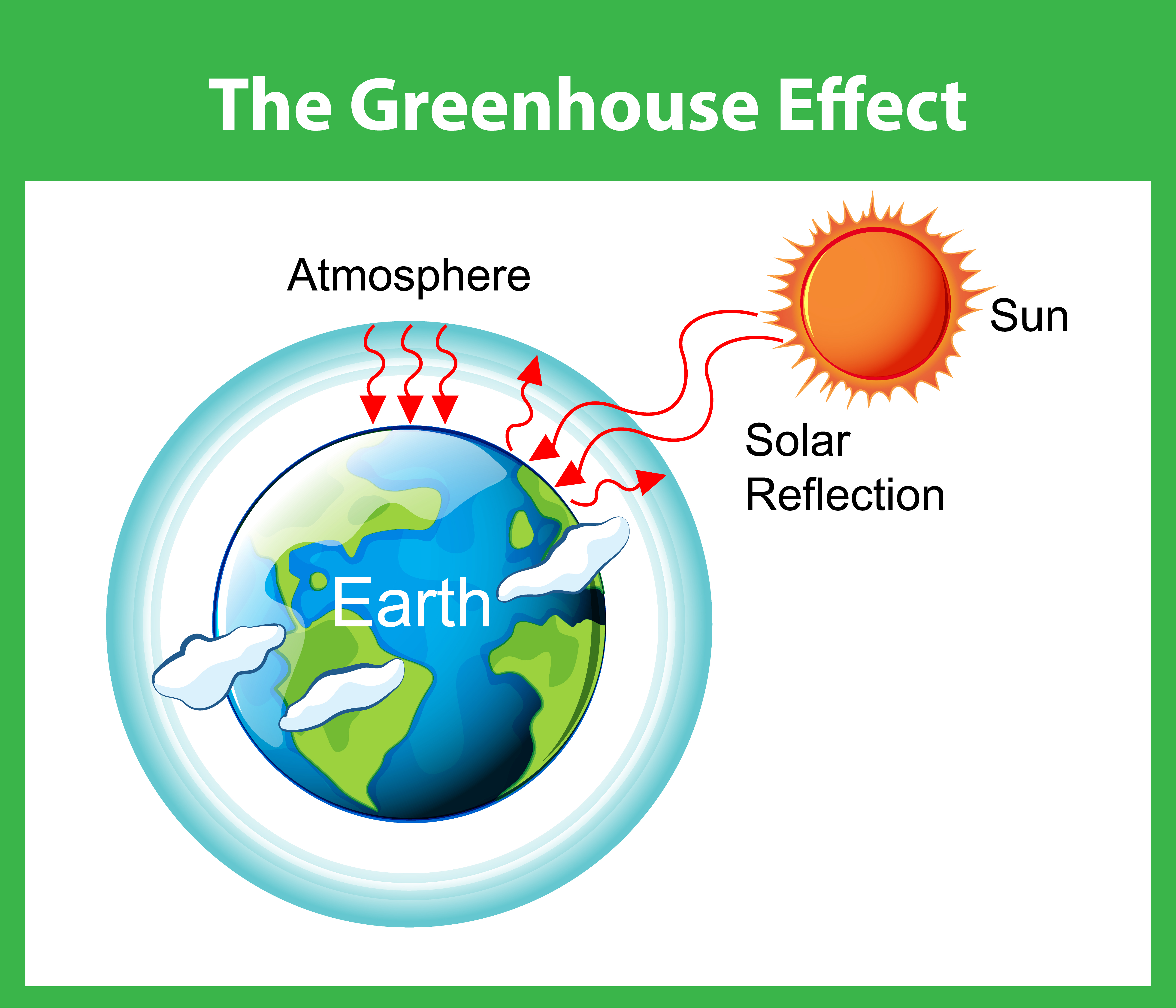
The Greenhouse Effect Life in a greenhouse? The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofGreenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees Celsius




File Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Wikimedia Commons




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
What could happen if this greenhouse effect changed the Earth's climate?The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is reradiated in all directions Since part of this reradiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperature above what it would be inThe Earth's natural greenhouse effect and account for about 90% of the total heatretaining capacity of the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to space The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process essential



Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library



The Green House Effect
Greenhouse effect, causing global warming The two most abundant gases in the atmosphere, nitrogen (comprising 78% of the dry atmosphere) and oxygen (comprising 21%), exert almost no greenhouse effect Instead, the greenhouse effect comes from molecules that are more complex and much less common Water vapour is the most important greenhouseGreenhouse effect Noun phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape greenhouse gas Noun gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere solar energyStudents observe teacherled demonstrations, and build and evaluate simple models to understand the greenhouse effect, the role of increased greenhouse gas concentration in global warming, and the implications of global warming for engineers, themselves and the Earth In an associated literacy activ




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Teaching Boxes are collections of classroomready and standardsaligned activities, content, and multimedia that build Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10 Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, and




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Although the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effectThe enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate changeThis effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount of greenhouseThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereAnalyze their greenhouse gas emissions Then they will participate in a greenhouse experimental demonstration and finally demonstrate their knowledge of the greenhouse effect using a puzzle (Appendix A Diagram) Prior Knowledge & Skills • Introductory knowledge of the greenhouse effect • Data gathering skills




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
WHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of theseThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouseA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3) Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
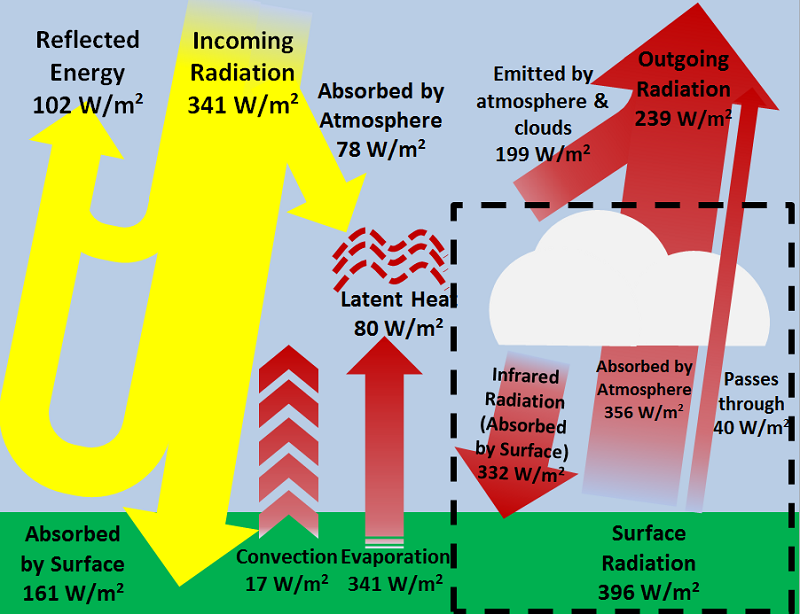
Ecology of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Coastal Wetlands Wetlands have the potential to absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide via photosynthesis, and flooded soils have low oxygen levels which decrease rates of decomposition to promote the retention of soil carbon However, the type of greenhouse gases emitted from wetlands varies by wetland The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally,The greenhouse effect of Earth From geometry, we can calculate the average solar flux at the top of the atmosphere It is approximately 343 W/m2 The earth has a much lower albedo than Venus (03), so the planet absorbs approximately 343 X 07 = 240 W/m2 By assuming that the incoming radiation equals the outgoing




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneGreenhouse Effect Teaching Box This teaching box provides resources related to the greenhouse effect It will help you teach how the greenhouse effect works, and how it prevents Earth from becoming a frozen ball of ice! ,008 greenhouse effect stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree greenhouse effect diagram commercial spraying water on plants greenhouse gas effect global warming posters sun earth diagram energy poster global warming global warming solutions sun radiating to a plant earth atmosphere greenhouse effect vector



1




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Find greenhouse effect diagram stock images in HD and millions of other royaltyfree stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the collection Thousands of new, highquality pictures added every dayGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph Fourier isActivity 11 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 7 – 9 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will do a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect, and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 The Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
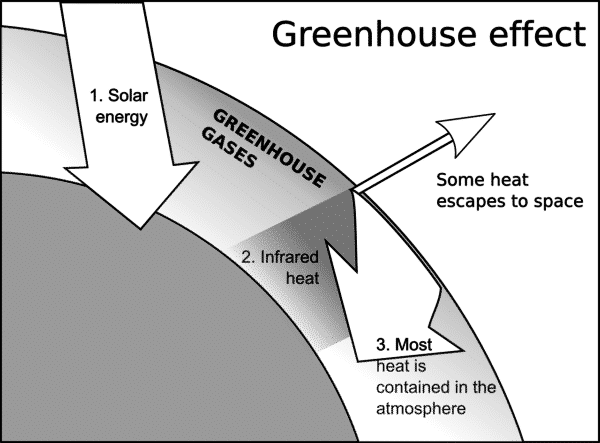
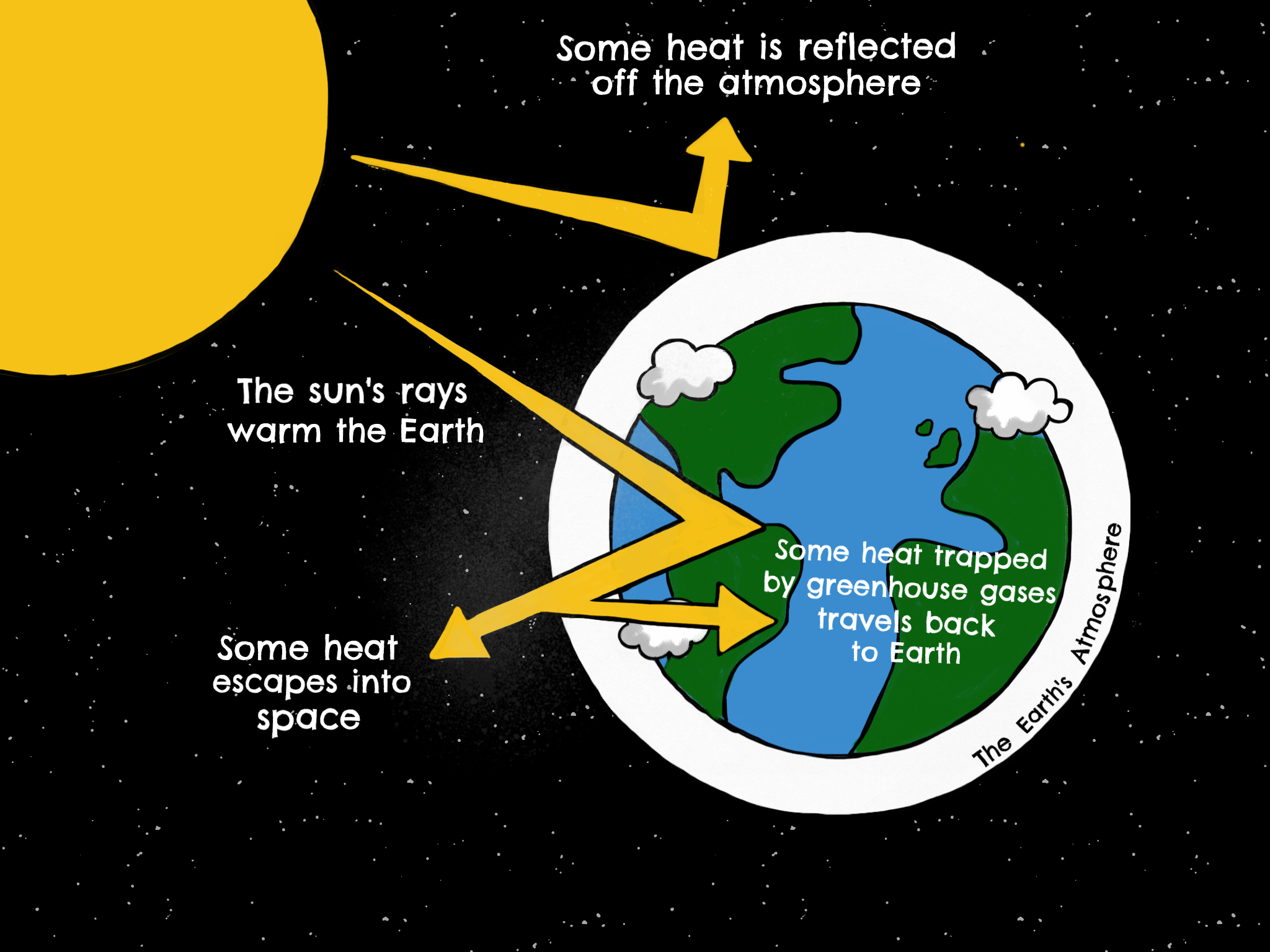
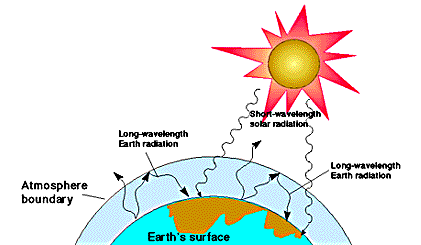
Contrasts Enhanced greenhouse effect is due to human activity Greenhouse effect is a natural process Enhanced greenhouse effect = less energy escapes back into space & increases earth's temperature by 018⁰C every decade Enhanced greenhouse effect = levels of gases in atmosphere, especially CO2 have increased à'blanket However, the actual existence of a greenhouse effect was already known In 14, Joseph Fourier had written that 'the temperature of the Earth can be augmented by the interposition of the atmosphere, because heat in the state of light finds less resistance in penetrating the air, than in repassing into the air when converted into nonluminous heat'Greenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards space




The Greenhouse Effect And Earth S Energy Budget Energy Education



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
This diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem The atmosphere, which has various kinds of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, little bit of carbon"Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of electricity, it also generates air pollutants including carbon dioxide (CO2The Greenhouse Effect Click Here for Transcript of The Greenhouse Effect video This diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram




The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Plans Greenhouse Gardening



Greenhouse Gas Vector Art Icons And Graphics For Free Download




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Climate Change Basics Ag Matters




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change



1




File The Green House Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons



Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



c News
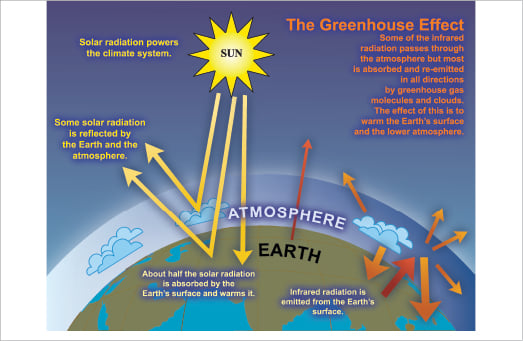



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids
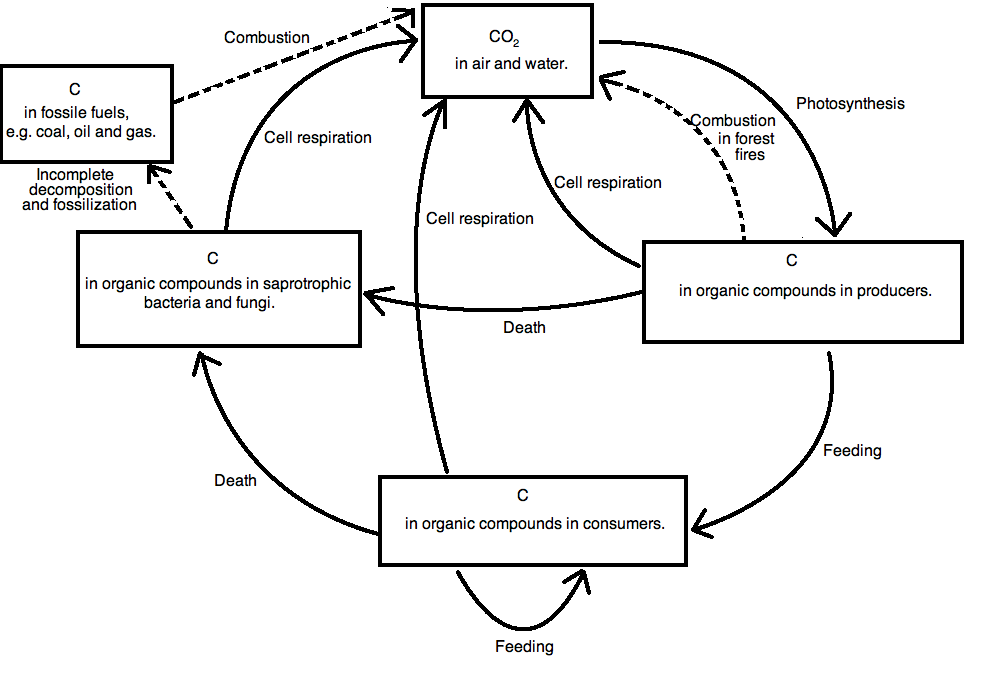



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg



The Greenhouse Effect




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In
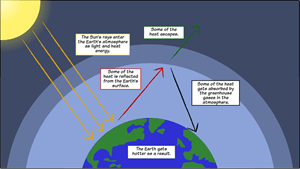



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
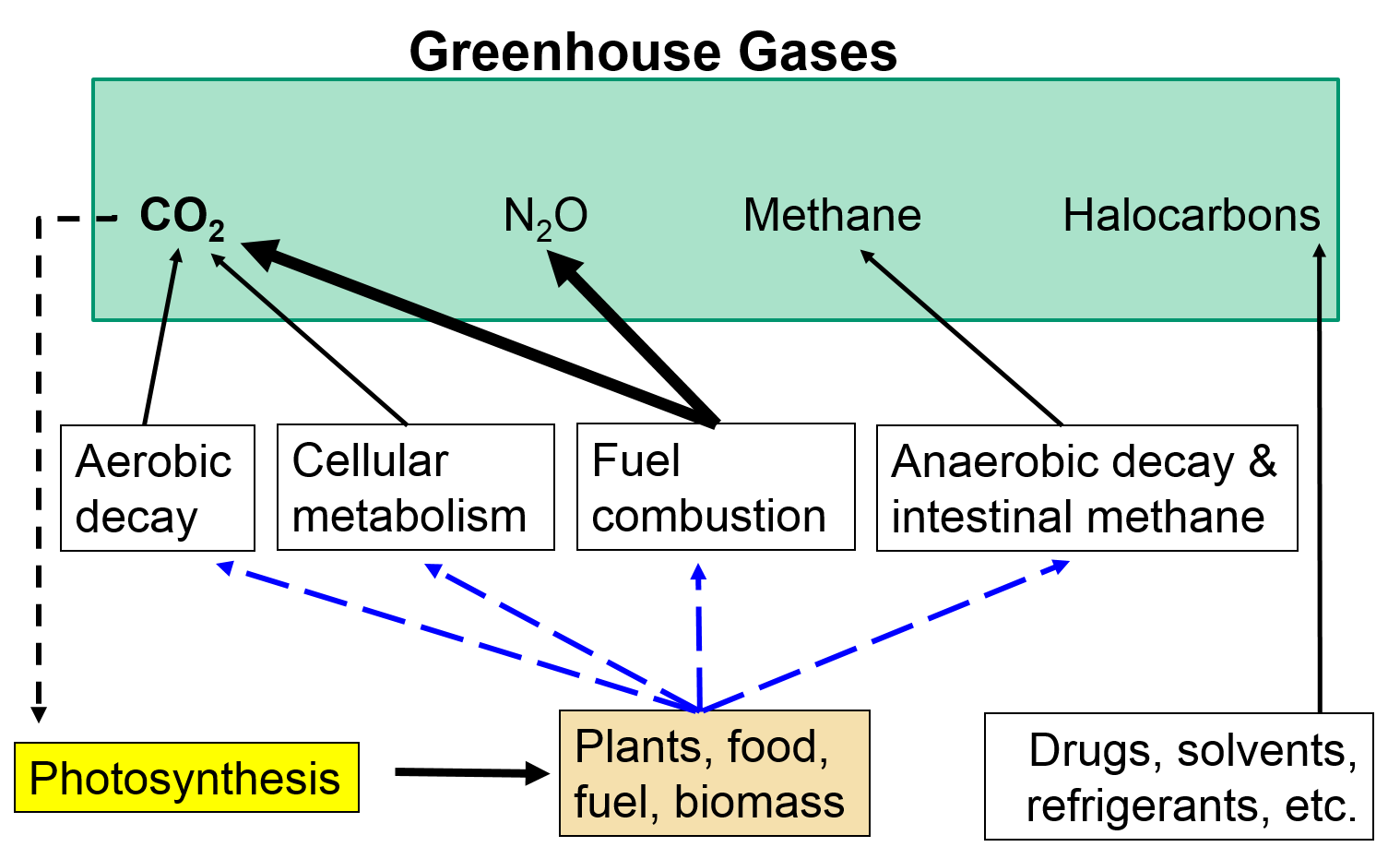



Greenhouse Gases Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
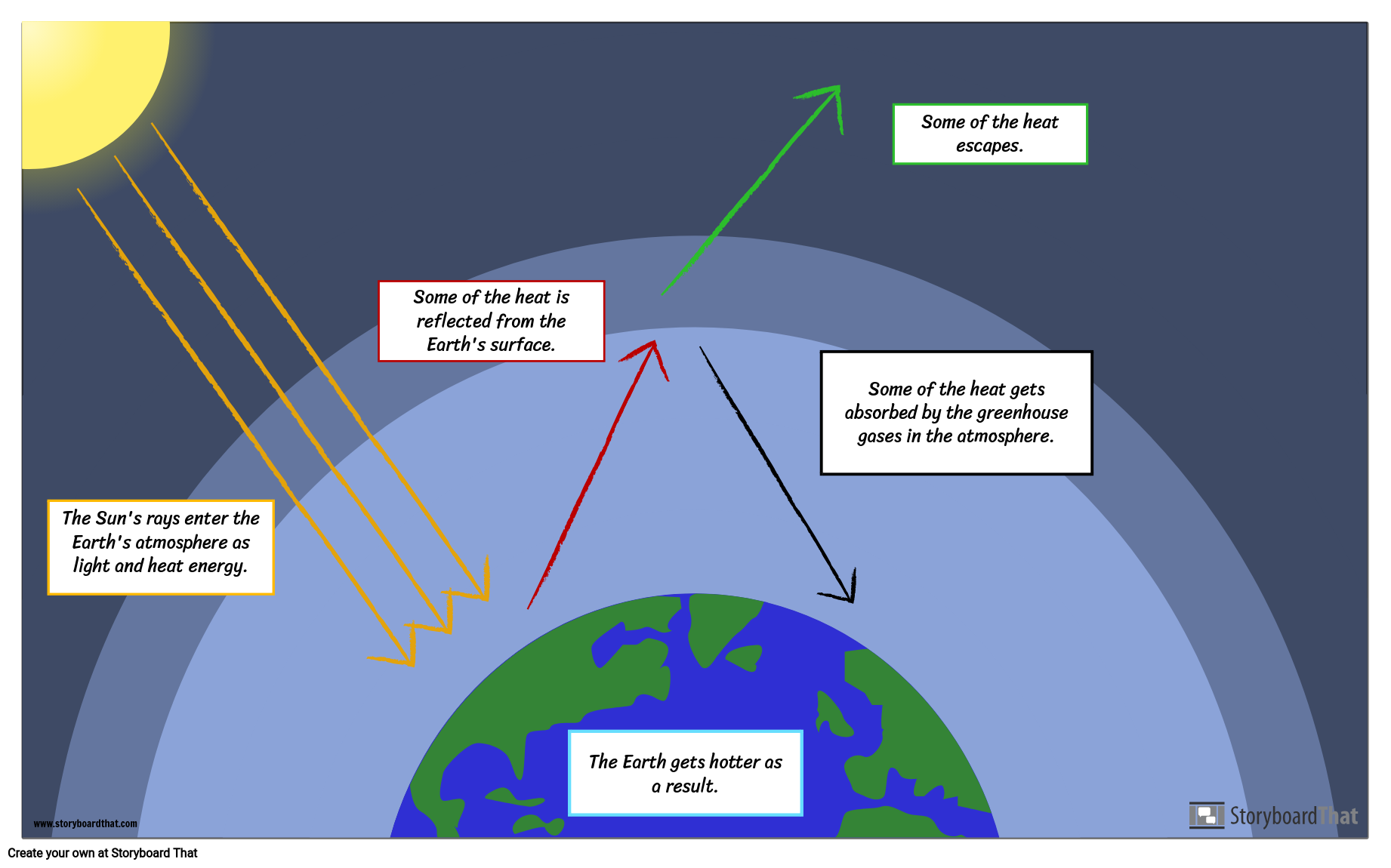



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
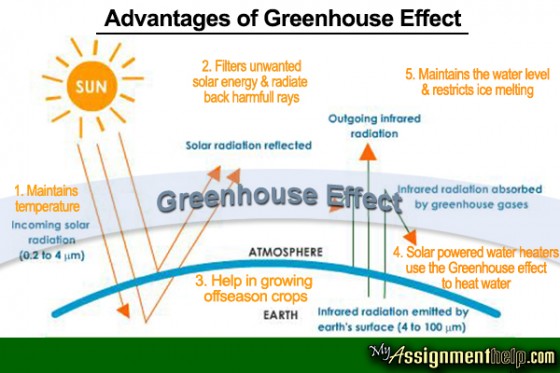



The Greenhouse Effect Know The Advantages And Disadvantages




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In



1




12 160 Greenhouse Effect Stock Photos And Images 123rf




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
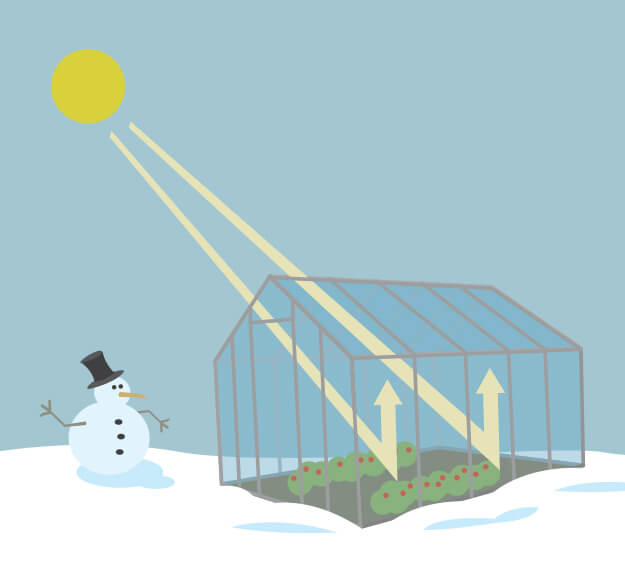




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



The Greenhouse Effect
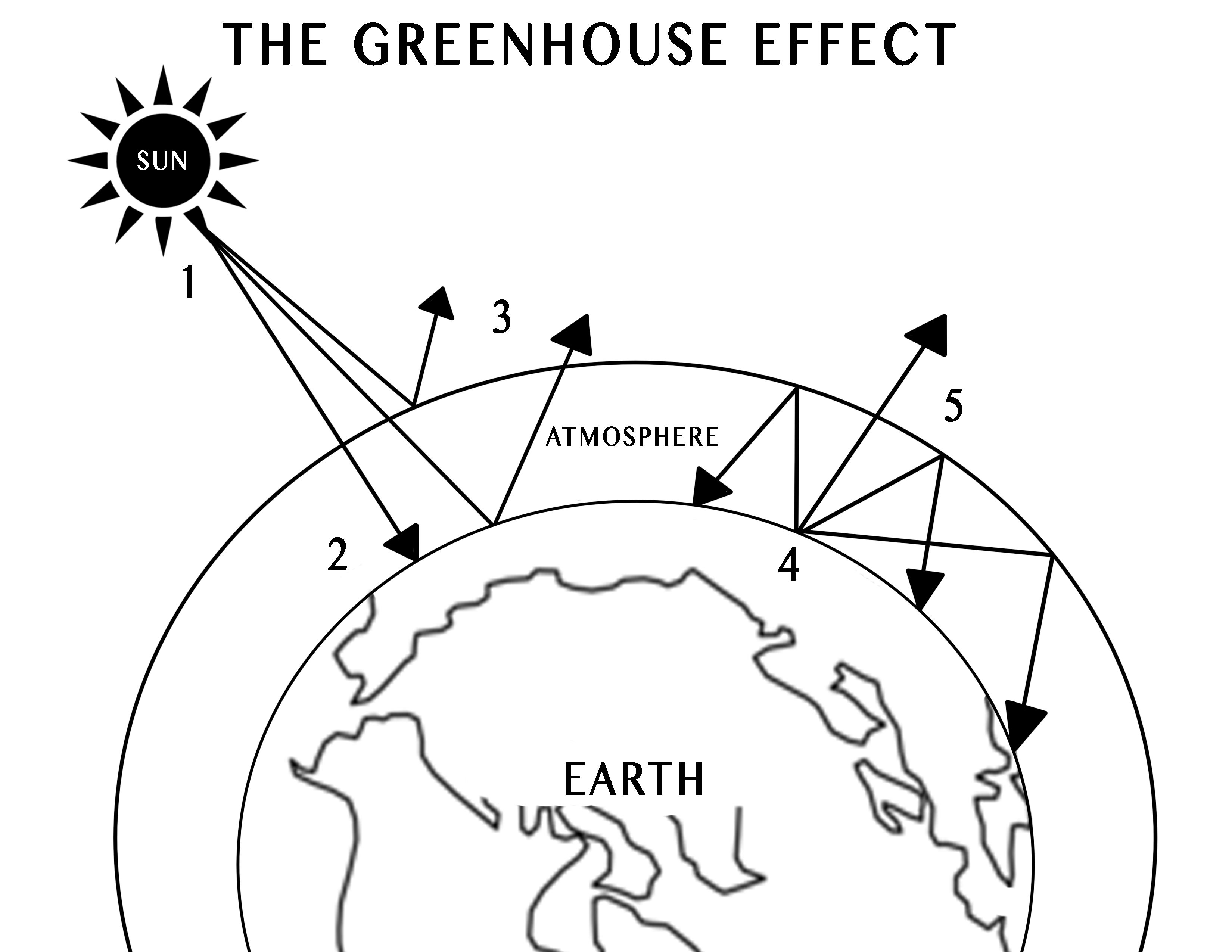



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena
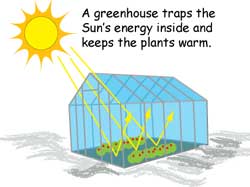



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
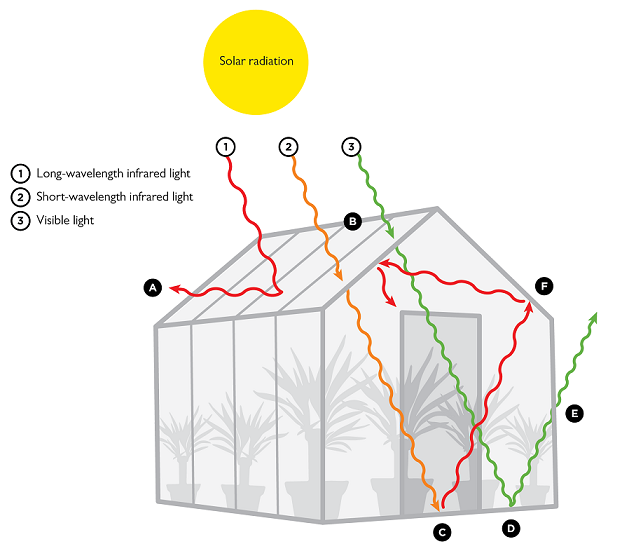



The Greenhouse Effect Comsol Blog




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
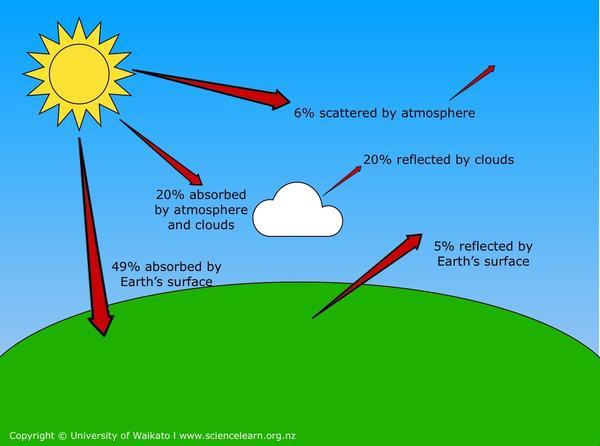



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters



Untitled Document




The Greenhouse Effect In Less Than 30 Seconds Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Vs Global Warming Drawing Easy Drawing For Kids Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Greenhouse Effect World101




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng
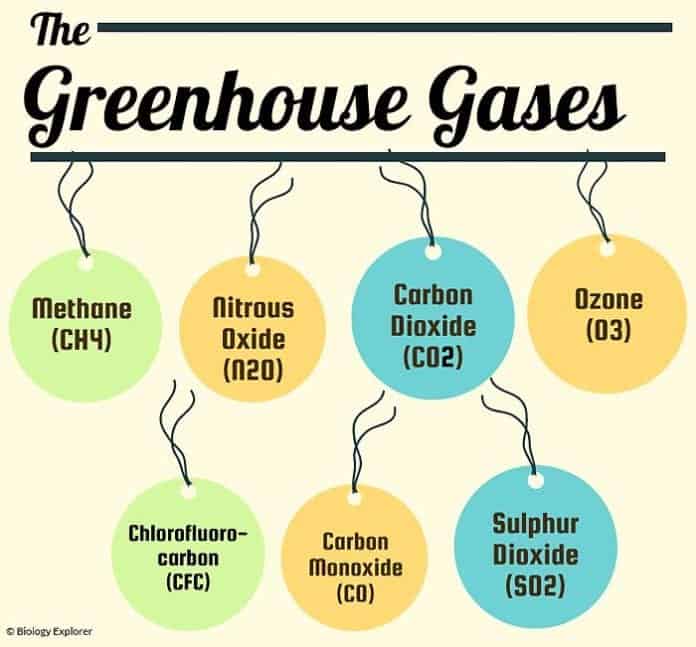



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change



The Greenhouse Effect



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿